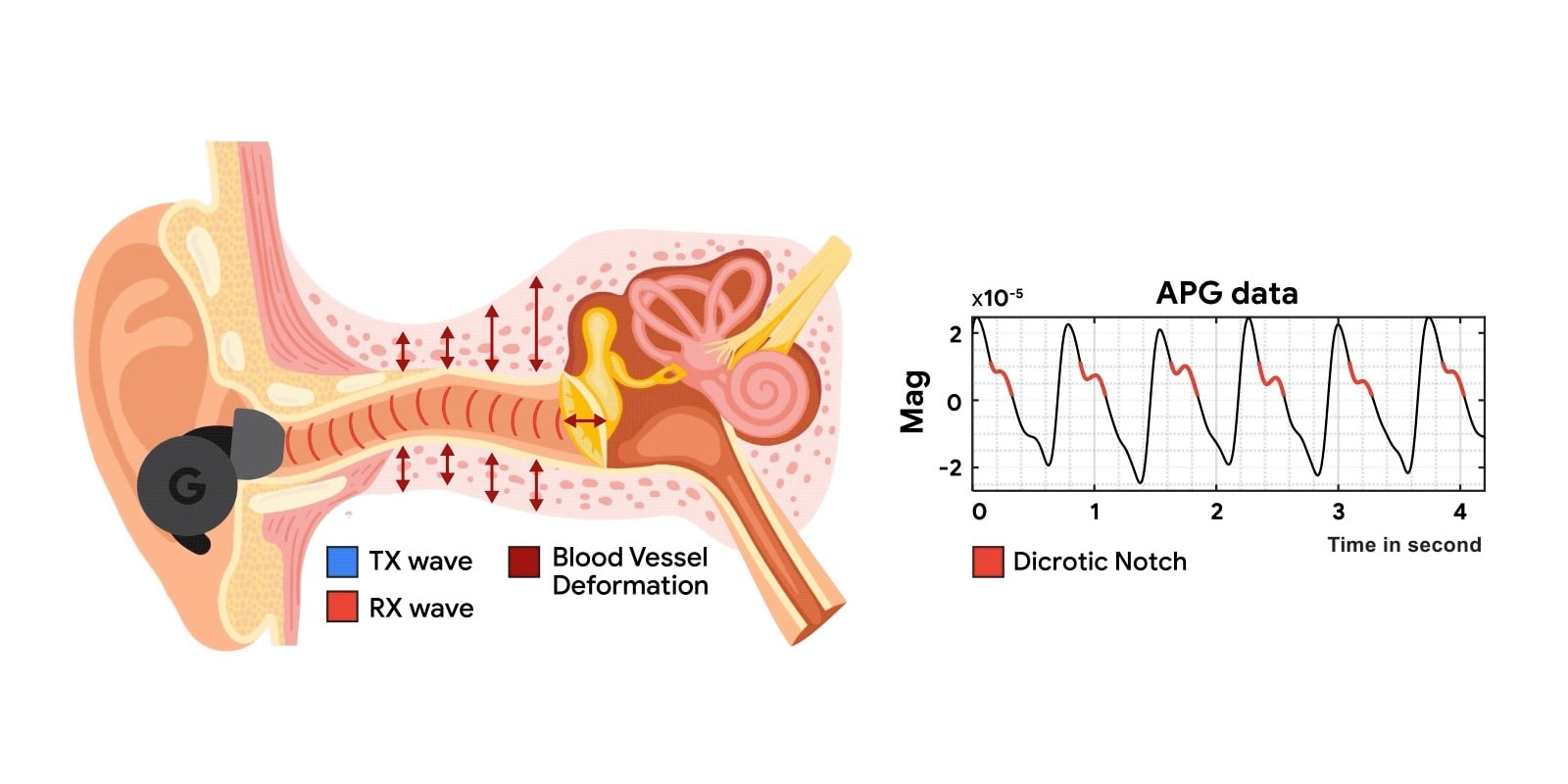
Google today detailed its research into audioplethysmography (APG) that adds heart rate sensing capabilities to active noise canceling (ANC) headphones and earbuds “with a simple software upgrade.”
Google says the “ear canal [is] an ideal location for health sensing” given that the deep ear artery “forms an intricate network of smaller vessels that extensively permeate the auditory canal.”
This audioplethysmography approach works by “sending a low intensity ultrasound probing signal through an ANC headphone’s speakers.”
This signal triggers echoes, which are received via on-board feedback microphones. We observe that the tiny ear canal skin displacement and heartbeat vibrations modulate these ultrasound echoes.
A model that Google created works to process that feedback into a heart rate reading, as well as heart rate variability (HRV) measurement. This technique works even with music playing and “bad earbuds seals.” However, it was impacted by body motion, and Google countered with a multi-tone approach that serves as a calibration tool to “find the best frequency that measures heart rate, and use only the best frequency to get high-quality pulse waveform.”
Google performed two sets of studies with 153 people that found APG “achieves consistently accurate heart rate (3.21% median error across participants in all activity scenarios) and heart rate variability (2.70% median error in inter-beat interval) measurements.”
Compared to existing HR sensors, it’s not impacted by skin tones. Ear canal size and “sub-optimal seal conditions” also do not impact accuracy. Google believes this is a better approach than putting traditional photoplethysmograms (PPG) and electrocardiograms (ECG) sensors, as well as a microcontroller, in headphones/earbuds:
…this sensor mounting paradigm inevitably adds cost, weight, power consumption, acoustic design complexity, and form factor challenges to hearables, constituting a strong barrier to its wide adoption.
Google closes on:
APG transforms any TWS ANC headphones into smart sensing headphones with a simple software upgrade, and works robustly across various user activities. The sensing carrier signal is completely inaudible and not impacted by music playing. More importantly, APG represents new knowledge in biomedical and mobile research and unlocks new possibilities for low-cost health sensing.
“APG is the result of collaboration across Google Health, product, UX and legal teams,” so this coming to Pixel Buds is far from guaranteed at this point.
Source: Google turned ANC earbuds into heart rate sensor

Robin Edgar
Organisational Structures | Technology and Science | Military, IT and Lifestyle consultancy | Social, Broadcast & Cross Media | Flying aircraft