Last week, privacy advocate (and very occasional Reg columnist) Alexander Hanff filed a complaint with the Irish Data Protection Commission (DPC) decrying YouTube’s deployment of JavaScript code to detect the use of ad blocking extensions by website visitors.
On October 16, according to the Internet Archives’ Wayback Machine, Google published a support page declaring that “When you block YouTube ads, you violate YouTube’s Terms of Service.”
“If you use ad blockers,” it continues, “we’ll ask you to allow ads on YouTube or sign up for YouTube Premium. If you continue to use ad blockers, we may block your video playback.”
YouTube’s Terms of Service do not explicitly disallow ad blocking extensions, which remain legal in the US [PDF], in Germany, and elsewhere. But the language says users may not “circumvent, disable, fraudulently engage with, or otherwise interfere with any part of the Service” – which probably includes the ads.
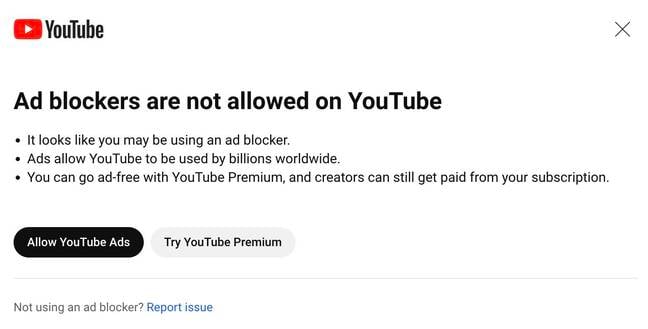
YouTube’s open hostility to ad blockers coincides with the recent trial deployment of a popup notice presented to web users who visit the site with an ad-blocking extension in their browser – messaging tested on a limited audience at least as far back as May.
In order to present that popup YouTube needs to run a script, changed at least twice a day, to detect blocking efforts. And that script, Hanff believes, violates the EU’s ePrivacy Directive – because YouTube did not first ask for explicit consent to conduct such browser interrogation.
[…]
Asked how he hopes the Irish DPC will respond, Hanff replied via email, “I would expect the DPC to investigate and issue an enforcement notice to YouTube requiring them to cease and desist these activities without first obtaining consent (as per [Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)] standard) for the deployment of their
spywaredetection scripts; and further to order YouTube to unban any accounts which have been banned as a result of these detections and to delete any personal data processed unlawfully (see Article 5(1) of GDPR) since they first started to deploy theirspywaredetection scripts.”Hanff’s use of strikethrough formatting acknowledges the legal difficulty of using the term “spyware” to refer to YouTube’s ad block detection code. The security industry’s standard defamation defense terminology for such stuff is PUPs, or potentially unwanted programs.
[…]
Hanff’s contention that ad-blocker detection without consent is unlawful in the EU was challenged back in 2016 by the maker of a detection tool called BlockAdblock. The software maker’s argument is that JavaScript code is not stored in the way considered in Article 5(3), which the firm suggests was intended for cookies.
Hanff disagrees, and maintains that “The Commission and the legislators have been very clear that any access to a user’s terminal equipment which is not strictly necessary for the provision of a requested service, requires consent.
“This is also bound by CJEU Case C-673/17 (Planet49) from October 2019 which *all* Member States are legally obligated to comply with, under the [Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union] – there is no room for deviation on this issue,” he elaborated.
“If a script or other digital technology is strictly necessary (technically required to deliver the requested service) then it is exempt from the consent requirements and as such would pose no issue to publishers engaging in legitimate activities which respect fundamental rights under the Charter.
“It is long past time that companies meet their legal obligations for their online services,” insisted Hanff. “This has been law since 2002 and was further clarified in 2009, 2012, and again in 2019 – enough is enough.”
Google did not respond to a request for comment.
Source: Privacy advocate challenges YouTube’s ad blocking detection • The Register

Robin Edgar
Organisational Structures | Technology and Science | Military, IT and Lifestyle consultancy | Social, Broadcast & Cross Media | Flying aircraft