[…]
after about 12 months of intensive investigation. Besides how the attackers learned of the hardware feature, the researchers still don’t know what, precisely, its purpose is. Also unknown is if the feature is a native part of the iPhone or enabled by a third-party hardware component such as ARM’s CoreSight
The mass backdooring campaign, which according to Russian officials also infected the iPhones of thousands of people working inside diplomatic missions and embassies in Russia, according to Russian government officials, came to light in June. Over a span of at least four years, Kaspersky said, the infections were delivered in iMessage texts that installed malware through a complex exploit chain without requiring the receiver to take any action.
With that, the devices were infected with full-featured spyware that, among other things, transmitted microphone recordings, photos, geolocation, and other sensitive data to attacker-controlled servers. Although infections didn’t survive a reboot, the unknown attackers kept their campaign alive simply by sending devices a new malicious iMessage text shortly after devices were restarted.
A fresh infusion of details disclosed Wednesday said that “Triangulation”—the name Kaspersky gave to both the malware and the campaign that installed it—exploited four critical zero-day vulnerabilities, meaning serious programming flaws that were known to the attackers before they were known to Apple. The company has since patched all four of the vulnerabilities, which are tracked as:
Besides affecting iPhones, these critical zero-days and the secret hardware function resided in Macs, iPods, iPads, Apple TVs, and Apple Watches. What’s more, the exploits Kaspersky recovered were intentionally developed to work on those devices as well. Apple has patched those platforms as well. Apple declined to comment for this article.
[…]
“This is no ordinary vulnerability,” Larin said in a press release that coincided with a presentation he made at the 37th Chaos Communication Congress in Hamburg, Germany. “Due to the closed nature of the iOS ecosystem, the discovery process was both challenging and time-consuming, requiring a comprehensive understanding of both hardware and software architectures. What this discovery teaches us once again is that even advanced hardware-based protections can be rendered ineffective in the face of a sophisticated attacker, particularly when there are hardware features allowing to bypass these protections.”
In a research paper also published Wednesday, Larin added:
If we try to describe this feature and how attackers use it, it all comes down to this: attackers are able to write the desired data to the desired physical address with [the] bypass of [a] hardware-based memory protection by writing the data, destination address and hash of data to unknown, not used by the firmware, hardware registers of the chip.
Our guess is that this unknown hardware feature was most likely intended to be used for debugging or testing purposes by Apple engineers or the factory, or was included by mistake. Since this feature is not used by the firmware, we have no idea how attackers would know how to use it
On the same day last June that Kaspersky first disclosed Operation Triangulation had infected the iPhones of its employees, officials with the Russian National Coordination Center for Computer Incidents said the attacks were part of a broader campaign by the US National Security Agency that infected several thousand iPhones belonging to people inside diplomatic missions and embassies in Russia, specifically from those representing NATO countries, post-Soviet nations, Israel, and China. A separate alert from the FSB, Russia’s Federal Security Service, alleged Apple cooperated with the NSA in the campaign. An Apple representative has denied the claim. Kaspersky researchers, meanwhile, have said they have no evidence corroborating the claim of involvement by either the NSA or Apple.
[…]
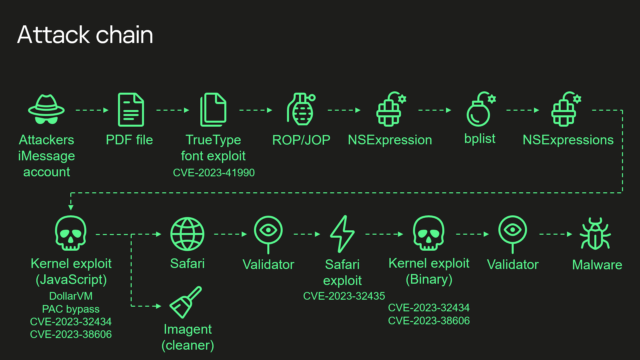
Kaspersky’s summary of the exploit chain is:
- Attackers send a malicious iMessage attachment, which is processed by the application without showing any signs to the user
- This attachment exploits vulnerability CVE-2023-41990 in the undocumented, Apple-only TrueType font instruction ADJUST for a remote code execution. This instruction existed since the early 90’s and the patch removed it.
- It uses return/jump oriented programming, multiple stages written in NSExpression/NSPredicate query language, patching JavaScriptCore library environment to execute a privilege escalation exploit written in JavaScript.
- This JavaScript exploit is obfuscated to make it completely unreadable and to minimize its size. Still it has around 11000 lines of code which are mainly dedicated to JavaScriptCore and kernel memory parsing and manipulation.
- It’s exploited JavaScriptCore’s debugging feature DollarVM ($vm) to get the ability to manipulate JavaScriptCore’s memory from the script and execute native API functions.
- It was designed to support old and new iPhones and included a Pointer Authentication Code (PAC) bypass for exploitation of newer models.
- It used an integer overflow vulnerability CVE-2023-32434 in the XNU’s memory mapping syscalls (mach_make_memory_entry and vm_map) to get read/write access to [the] whole physical memory of the device from the user level.
- It uses hardware memory-mapped I/O (MMIO) registers to bypass Page Protection Layer (PPL). This was mitigated as CVE-2023-38606.
- After exploiting all the vulnerabilities, the JavaScript exploit can do whatever it wants to the device and run spyware, but attackers chose to: a) launch the imagent process and inject a payload that cleans the exploitation artifacts from the device; b) run the Safari process in invisible mode and forward it to the web page with the next stage.
- Web page has the script that verifies the victim and, if the checks pass, it receives the next stage—the Safari exploit.
- Safari exploit uses vulnerability CVE-2023-32435 to execute a shellcode.
- Shellcode executes another kernel exploit in the form of mach object file. It uses the same vulnerabilities CVE-2023-32434 and CVE-2023-38606, it’s also massive in size and functionality, but it is completely different from the kernel exploit written in JavaScript. Only some parts related to exploitation of the above-mentioned vulnerabilities are the same. Still most of its code is also dedicated to the parsing and manipulation of the kernel memory. It has various post-exploitation utilities, which are mostly unused.
- Exploit gets root privileges and proceeds to execute other stages responsible for loading of spyware. We already covered these stages in our previous posts.
Wednesday’s presentation, titled What You Get When You Attack iPhones of Researchers, is a further reminder that even in the face of innovative defenses like the one protecting the iPhone kernel, ever more sophisticated attacks continue to find ways to defeat them.
[…]
Source: 4-year campaign backdoored iPhones using possibly the most advanced exploit ever | Ars Technica
It also shows that closed source software is an immense security threat – even with the threat exposed it’s almost impossible to find out what happened and how to fix it – especially without the help of the manufacturer

Robin Edgar
Organisational Structures | Technology and Science | Military, IT and Lifestyle consultancy | Social, Broadcast & Cross Media | Flying aircraft