Project Overview
The FAA’s Remote ID requirement, which became mandatory for most drones in September 2023, means every compliant drone now broadcasts its location, pilot position, and identification data via WiFi or Bluetooth. While this regulation was designed for safety and accountability (or to violate pilot privacy 😊), it also creates an unprecedented opportunity for personal airspace awareness.
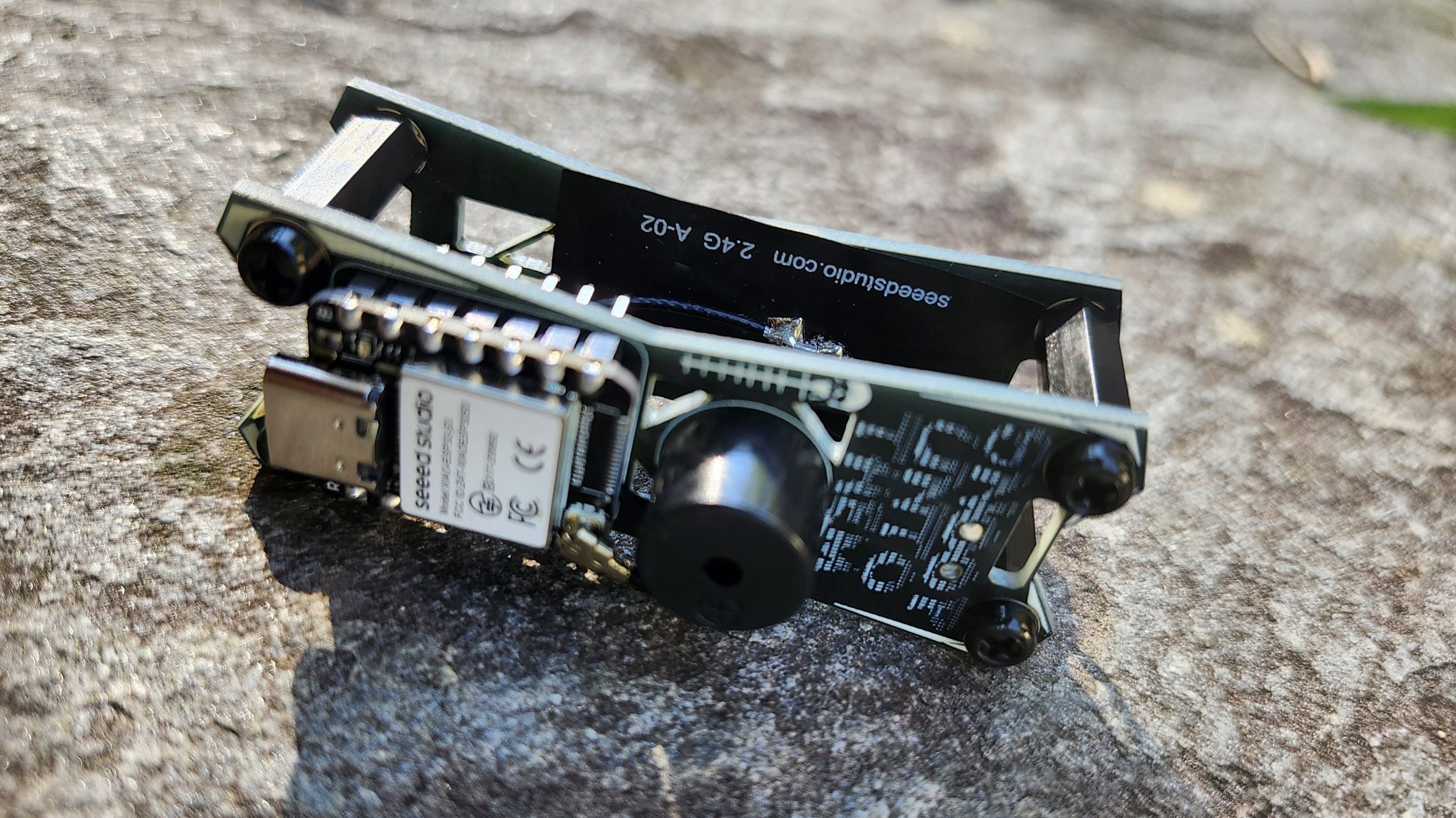
This project harnesses that data stream to create a comprehensive detection and tracking system that puts you in control of knowing what’s flying overhead. Built around the powerful dual-core Xiao ESP32 S3 microcontroller, the system captures Remote ID transmissions on both WiFi and Bluetooth simultaneously, feeding the data into a sophisticated Python Flask web application that provides real-time visualization and logging.
But here’s where it gets really interesting: the system also integrates with Meshtastic networks, allowing multiple detection nodes to share information across a mesh network. This means you can deploy several ESP32 nodes across your property or neighborhood and have them all contribute to a unified picture of drone activity in your area.
Why This Project Matters
Remote ID represents a fundamental shift in airspace transparency. For the first time, civilian drones are required to broadcast their identity and location continuously. This creates opportunities for:
- Privacy Protection: Know when drones are operating near your property and who is operating them
- Personal Security: Monitor activity around sensitive locations like your home or business
- Community Awareness: Share drone activity information with neighbors through mesh networks
- Research: Understand drone traffic patterns and airspace usage in your area
- Education: Learn about wireless protocols and modern airspace management
The key difference between this system and commercial drone detection
solutions is that it puts the power of airspace awareness directly in your
hands, using affordable hardware and open-source software.
While you can build this project using off-the-shelf ESP32 development boards, I’ve designed custom PCBs specifically optimized for Remote ID detection integration with Meshtastic that are that are available on my Tindie store. Thank you PCBway for the awesome boards! The combination of their top tier quality, competitive pricing, fast turnaround times, and stellar customer service makes PCBWay the go-to choice for professional PCB fabrication, whether you’re prototyping innovative mesh detection systems or scaling up for full production runs.
https://www.pcbway.com/
Step 1: Hardware Preparation
If using custom MeshDetect boards from Tindie:
- Boards come pre-assembled, flashed, and tested
- Includes Stock 915mhz and 2.4ghz antennas
- USB-C programming interface ready to use
If building with standard ESP32 S3:
- Xiao ESP32 S3 development board recommended
- USB-C cable for connection and power
- Optional upgraded3 2.4GHz antenna for better range
- Optional Heltec Lora V3 for Mesthastic Integration
Step 2: Firmware Installation
To install the firmware onto your device, follow these steps:
1. Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/colonelpanichacks/drone-mesh-mapper
Open the project in PlatformIO: You can use the PlatformIO IDE (in VS Code) or the PlatformIO CLI.
2.Select the correct environment:
This project uses the remotied_mesh_dualcore sketch, which enables both BLE and Wi-Fi functionality.Make sure the platformio.ini environment is set to remoteid_mesh_dualcore.
3. Connect you device via usb and flash
Upload the firmware:
- In the IDE, select the
remoteid_mesh_dualcore environment and click the “Upload” button.
3. Sofware Installation
Install Python dependencies:
- flask>=2.0.0
- flask-socketio>=5.0.0
- requests>=2.25.0
- urllib3>=1.26.0
- pyserial>=3.5
Run the detection system:
python mapper.py
The web interface automatically opens at http://localhost:5000
Step 4: Device Configuration
1. Connect ESP32 via USB-C
2. Select the correct serial port in the web interface
3. Click “Connect” to start receiving data
4. Configure device aliases and settings as needed
How It Works
The ESP32 S3’s dual-core architecture allows simultaneous monitoring of both WiFi and Bluetooth Remote ID transmissions:
- Core 0 handles WiFi monitoring in promiscuous mode, capturing Remote ID data embedded in beacon frames and processing Neighbor Awareness Networking transmissions on channel 6 by default.
- Core 1 continuously scans for Bluetooth LE advertisements containing Remote ID data, supporting both BT 4.0 and 5.0 protocols with optimized low-power scanning.
- Both cores feed detected Remote ID data into a unified JSON output stream via USB serial at 115200 baud. The firmware is based on Cemaxacuter’s excellent Remote ID detection work, enhanced with dual-core operation.
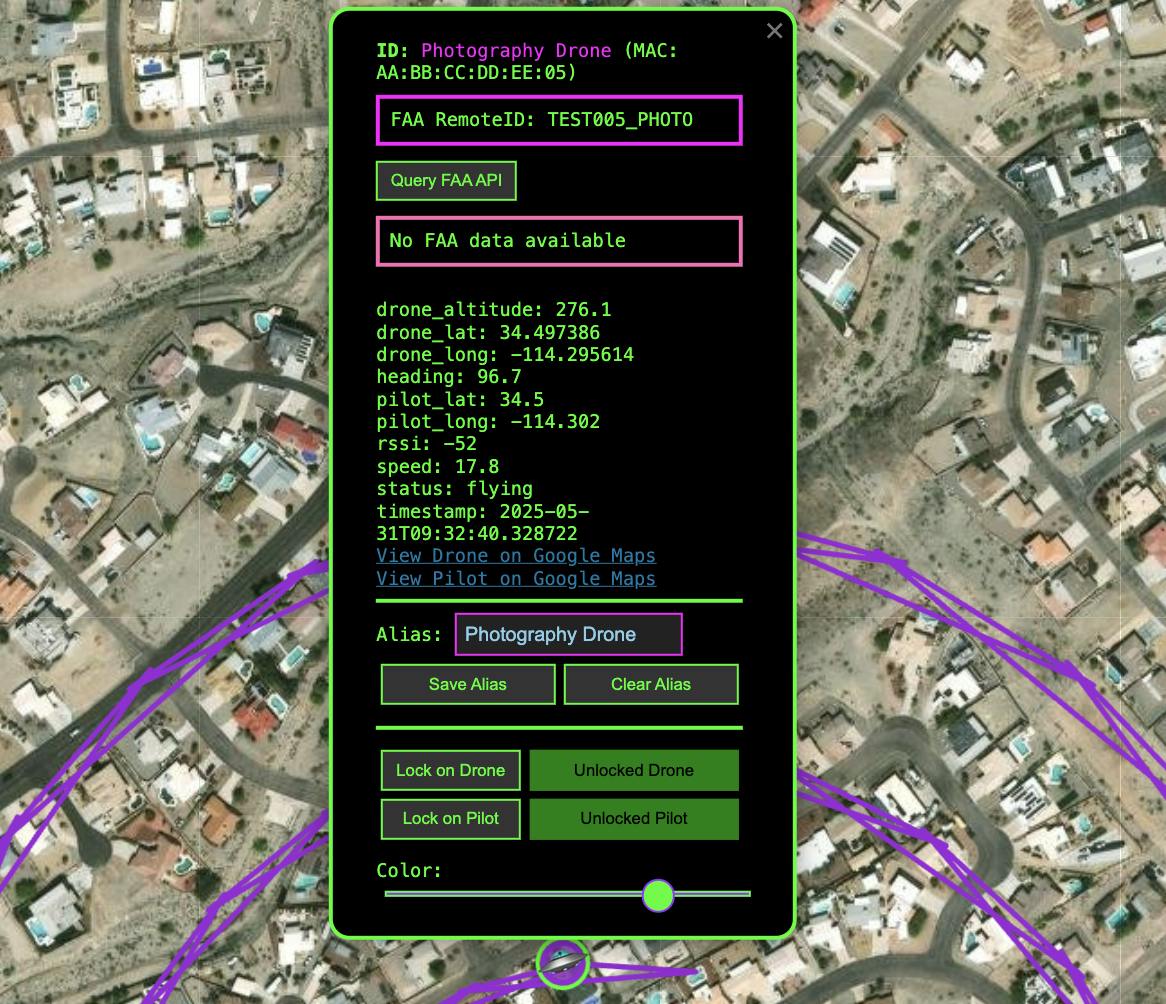
- The Python Flask web application receives this data and provides real-time visualization on an interactive map, automatic logging to CSV and KML files, FAA database integration for aircraft registration lookups, support for up to 3 ESP32 devices simultaneously, live data streaming via WebSocket, and comprehensive export functions.
Meshtastic Integration: Distributed Detection
One of the most exciting features is Meshtastic integration. The ESP32 firmware can send compact detection messages over UART to a connected Meshtastic device. This enables:
- Distributed Monitoring: Multiple detection nodes sharing data across your property or neighborhood
- Extended Range: Mesh networking extends effective coverage area beyond single-device limitations
- Redundancy: Multiple nodes provide backup coverage if one device fails
- Low-Power Operation: Meshtastic’s LoRa radios enable remote deployment without constant power
- Community Networks: Integration with existing Meshtastic mesh networks for broader awareness
- Messages sent over the mesh network use a compact format optimized for LoRa bandwidth constraints:
Features in Action
Real-Time Detection and Mapping
The web interface provides a Google Maps-style view with drone markers showing current aircraft positions, pilot markers indicating operator locations, color-coded flight paths derived from device MAC addresses, signal strength indicators showing detection quality, and automatic cleanup removing stale data after 5 minutes.
Data Export and Analysis
The system continuously generates multiple data formats including timestamped CSV logs perfect for spreadsheet analysis, Google Earth compatible KML files with flight path visualization featuring individual drone paths color-coded by device and timestamped waypoints, and JSON API providing real-time data access for custom integrations with RESTful endpoints and WebSocket streams.
FAA Database Integration
One of the most powerful features is automatic FAA registration lookup that queries the FAA database using detected Remote ID information, caches results to minimize API calls and improve performance, enriches detection data with aircraft registration details, and includes configurable rate limiting to respect API guidelines.
Multi-Device Coordination
The system supports up to three ESP32 devices simultaneously with automatic device discovery and connection, individual device health monitoring, load balancing across multiple receivers, and unified data view combining all devices.
Performance and Optimization
Reception Range
Testing has shown effective detection ranges of 5 Km in urban environments, 10-15 kilometers in open areas with good antennas, overlapping coverage that eliminates dead zones when using multiple devices, and significant improvement with external antennas compared to built-in antennas.
System Resources
The Python application is optimized for continuous operation with efficient memory management for large datasets, automatic log rotation to prevent disk space issues, WebSocket connection pooling for multiple clients, and configurable data retention policies.
For remote deployments, Meshtastic integration enables off-grid operation, webhook retry logic ensures reliable alert delivery, local data storage prevents data loss during network outages, and bandwidth optimization handles limited connections.
Privacy and Security Considerations
This system puts powerful airspace monitoring capabilities in individual hands, but it’s important to use it responsibly. The detection data contains location information about both drones and their operators, so implement appropriate data retention policies and be aware of local privacy regulations.
For network security, remember that the Flask development server is not production-ready, so consider a reverse proxy for production use and implement authentication for sensitive deployments. Use HTTPS for webhook communications and monitor for unauthorized access attempts.
The system enables you to know what’s flying over your property while respecting the legitimate privacy expectations of drone operators. It’s about transparency and awareness, not surveillance.
Conclusion
This Remote ID detection system represents a significant step forward in personal airspace awareness. The combination of dual-core ESP32 processing, comprehensive web-based interface, Meshtastic mesh integration, and professional data export features creates a platform that’s both accessible to makers and powerful enough for serious privacy protection applications.
The availability of custom-designed PCBs on Tindie removes the barrier of hardware design, while the open-source firmware and software ensure complete customizability. Whether you’re building a single-node setup for personal property monitoring or deploying a mesh network for neighborhood-wide awareness, this system provides the foundation for comprehensive drone detection and tracking.
As more drones come online with Remote ID compliance, having your own detection system becomes increasingly valuable for maintaining privacy and situational awareness of your local airspace
Resources and Links
Mesh Mapper Github : https://github.com/colonelpanichacks/drone-mesh-mapper
Mesh Detect Github (all firmware for Mesh Detect boards: https://github.com/colonelpanichacks/mesh-detect
Mesh Detect SMA mount clip SMA mount clip for the Mesh Destect board by OrdoOuroboros https://www.printables.com/model/1294183-mesh-detect-board-sma-mount
Build Your Own
Ready to start monitoring your local airspace? The combination of affordable hardware, open-source software, and comprehensive documentation makes this project accessible to makers of all skill levels. Start with a single ESP32 device to learn the system, then expand to multiple nodes and Meshtastic integration as your privacy protection needs grow.
The future of airspace monitoring is distributed, affordable, and puts control back in the hands of individuals and communities. Join the movement building these next-generation detection systems!